Accounting एक ऐसा Process है जिसके माध्यम से किसी व्यवसाय/कारोबार (Business) का वित्तीय लेन-देन (Financial Transactions) को रिकॉर्ड किया जाता है, उनका वर्गीकरण (classification), सारांश (summarization) और विश्लेषण (analysis) किया जाता है। इसका उद्देश्य व्यवसाय की आर्थिक स्थिति को समझना और रिपोर्ट तैयार करना होता है।
Accounting को तीन मुख्य प्रकारों में बाँटा गया है:
- Personal Accounting (व्यक्ति खाता)
- Real Accounting (वास्तविक खाता)
- Nominal Accounting (नाम मात्र खाता)
Personal Accounting (व्यक्ति खाता)
Personal Account ऐसे account होते हैं जो किसी व्यक्ति (person), कंपनी (company), या संगठन (organization) से जुड़े होते हैं – जिनसे business का direct लेन-देन होता है। जैसे Wasim a/c, Ram a/c, Rahman a/c, WSM Computer Institute, Bank a/c, Shakila & Iqbal Hussain Trust, etc.
Golden Rule : “जिसे पैसा मिलता है, उसे डेबिट करो; जिसे पैसा दिया जाता है, उसे क्रेडिट करो।”
Personal Account को तीन main categories में divide किया गया है:
- Natural Person Account (प्राकृतिक व्यक्ति खाता)
- Artificial Person Account (कृत्रिम व्यक्ति खाता)
- Representative Personal Account (प्रतिनिधि व्यक्तिगत खाता)
Natural Person Account (प्राकृतिक व्यक्ति खाता)
Natural Person Account : इस type का account किसी real human being यानी असली व्यक्ति से related होता है। जब business किसी इंसान से लेन-देन करता है, तो हम उसके नाम पर Natural Person Account बनाते हैं।
Examples: Rahman a/c, Ram’s A/c, Sita’s A/c, Mohan’s A/c, Wasim a/c.
Artificial Person Account (कृत्रिम व्यक्ति खाता)
ये accounts उन entities के लिए बनाए जाते हैं जो इंसान नहीं होतीं, लेकिन law उन्हें व्यक्ति की तरह treat करता है। जैसे – organization, banks, companies, societies, trust आदि।
Business जब इनसे लेन-देन करता है, तो Artificial Person Account create होता है।
Examples: SBI Bank A/c, Reliance Ltd A/c, LIC A/c, WSM Computer Institute a/c, Tata a/c
Representative Personal Account (प्रतिनिधि व्यक्तिगत खाता)
Representative Personal Account : इस तरह का account किसी individual को directly show नहीं करता, लेकिन किसी व्यक्ति से जुड़े हुए income या expense को represent करता है।
जैसे – अगर किसी employee को salary देनी बाकी है, तो वो Outstanding Salary A/c कहलाएगा, और ये Representative Account होगा।
Examples: Outstanding Salary A/c, Outstanding Rent A/c, Prepaid Insurance A/c, Accrued Commission A/c
Real Accounting (वास्तविक खाता)
Real Account ऐसे accounts होते हैं जो किसी संपत्ति (assets) या संसाधन (resources) से जुड़े होते हैं।
इन खातों में हम उन चीजों का record रखते हैं जो business में use की जाती हैं, जैसे – cash, building, machinery, furniture आदि।
Tangible Assets (साक्षात संपत्ति)
ये वो संपत्तियाँ हैं जिन्हें आप छू सकते हैं:
- Cash Account (कैश खाता) – नकद लेन-देन
- Bank Account (बैंक खाता) – बैंक से जुड़ा लेन-देन
- Building Account (बिल्डिंग खाता) – इमारत से जुड़ी खरीद/बिक्री
- Furniture Account (फर्नीचर खाता) – कुर्सी, टेबल आदि
- Machinery Account (मशीनरी खाता) – मशीनें
- Land Account (भूमि खाता) – जमीन
- Vehicle Account (वाहन खाता) – बाइक, कार आदि
- Stock/Inventory Account (भंडार खाता) – माल-सामान
Intangible Assets (अमूर्त संपत्ति)
ये वो संपत्तियाँ हैं जिन्हें आप छू नहीं सकते लेकिन उनके value होती है:
- Goodwill Account (साख खाता)
- Patent Account (पेटेंट खाता)
- Trademark Account (ट्रेडमार्क खाता)
- Copyright Account (कॉपीराइट खाता)
- Software Account (सॉफ्टवेयर खाता)
Nominal Account (नाममात्र खाता)
Nominal Account ऐसे खाते होते हैं जो किसी income (आय), expense (खर्च), loss (हानि) या gain (लाभ) को दिखाते हैं।
ये खाते temporary होते हैं और प्रत्येक accounting year के अंत में इनका balance Profit & Loss Account में transfer कर दिया जाता है।
Example : Salary A/c (वेतन खाता), Rent A/c (किराया खाता), Electricity A/c (बिजली बिल खाता), Wages A/c (मजदूरी खाता), Stationery A/c (कागज़, पेन आदि), Loss by Fire A/c (आग से हानि), Bad Debts A/c (बकाया डूब गई रकम),
Golden Rules of Accounting
Accounting में Golden Rules of Accounting बहुत ही महत्वपूर्ण हैं — इन rules से हम ये सीखते हैं कि किसी भी लेन-देन में किस account को कब Debit करना है और कब किस account को Credit करना है।
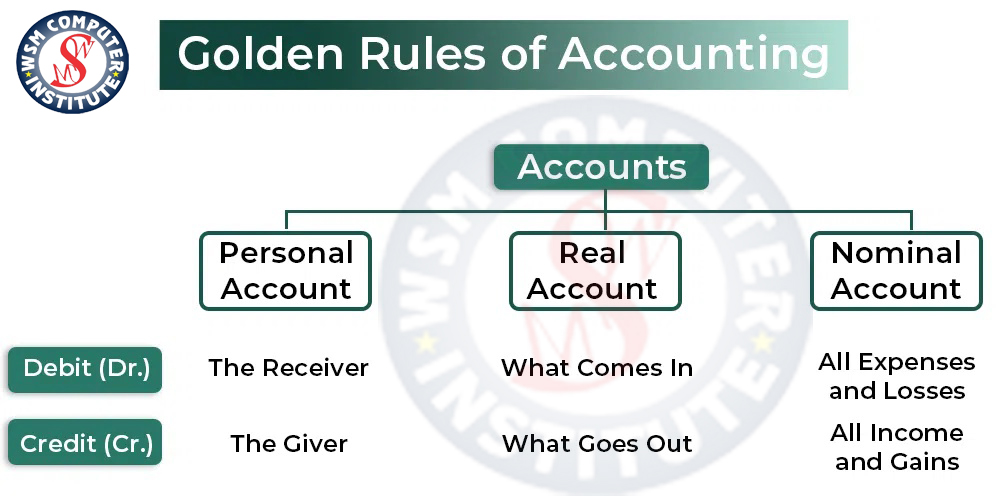
1. Personal Account (व्यक्तिगत खाता)
Rule:
👉 Debit the Receiver, Credit the Giver
जो ले रहा है उसे Debit, जो दे रहा है उसे Credit
2. Real Account (वास्तविक खाता)
Rule:
👉 Debit what comes in, Credit what goes out
जो चीज़ अंदर आए उसे Debit, जो जाए उसे Credit
3. Nominal Account (नाममात्र खाता)
Rule:
👉 Debit all expenses and losses, Credit all incomes and gains
खर्च/हानियाँ Debit, आमदनी/लाभ Credit
1. Cash Purchase of Goods
Transaction: Purchased goods worth ₹5,000 in cash.
- Entry:
- Debit: Purchases Account ₹5,000 (because goods are purchased, which is an expense)
- Credit: Cash Account ₹5,000 (because cash is paid)
2. Purchase of Goods on Credit
Transaction: Purchased goods worth ₹15,000 on credit.
- Entry:
- Debit: Purchases Account ₹15,000 (because goods are purchased, which is an expense)
- Credit: Accounts Payable (or Supplier Account) ₹15,000 (because a liability is created)
3. Purchase of Goods Paid Through Bank
Transaction: Purchased goods worth ₹18,000 from a supplier, and the payment was made via bank transfer.
- Entry:
- Debit: Purchases Account ₹18,000 (because goods are purchased, which is an expense)
- Credit: Bank Account ₹18,000 (because payment is made from the bank)
4. Cash Sale of Goods
Transaction: Sold goods worth ₹10,000 in cash.
- Entry:
- Debit: Cash Account ₹10,000 (because cash is received)
- Credit: Sales Account ₹10,000 (because income is generated from sales)
5. Sale of Goods on Credit
Transaction: Sold goods worth ₹12,000 on credit to a customer.
- Entry:
- Debit: Accounts Receivable (or Customer Account) ₹12,000 (because a receivable is created)
- Credit: Sales Account ₹12,000 (because sales income is generated)
6. Sale of Goods Paid Through Bank
Transaction: Sold goods worth ₹25,000 to a customer, and the customer paid via bank transfer.
- Entry:
- Debit: Bank Account ₹25,000 (because cash is received in the bank)
- Credit: Sales Account ₹25,000 (because sales income is generated)
7. Payment of Rent
Transaction: Paid ₹3,000 as rent.
- Entry:
- Debit: Rent Expense Account ₹3,000 (because rent is an expense)
- Credit: Cash Account ₹3,000 (because cash is paid)
8. Loan Received from Bank
Transaction: Received a loan of ₹50,000 from the bank.
- Entry:
- Debit: Cash Account ₹50,000 (because cash is received)
- Credit: Bank Loan Account ₹50,000 (because a liability is created)
9. Payment to Supplier
Transaction: Paid ₹4,000 to a supplier.
- Entry:
- Debit: Accounts Payable (or Supplier Account) ₹4,000 (because the liability decreases)
- Credit: Cash Account ₹4,000 (because cash is paid)
10. Purchase on Credit
Transaction: Purchased goods worth ₹7,000 on credit.
- Entry:
- Debit: Purchases Account ₹7,000 (because goods are purchased, which is an expense)
- Credit: Accounts Payable (or Supplier Account) ₹7,000 (because the liability increases)
11. Depreciation of Asset
Transaction: Depreciation of ₹2,000 on machinery.
- Entry:
- Debit: Depreciation Expense Account ₹2,000 (because depreciation is an expense)
- Credit: Accumulated Depreciation Account ₹2,000 (because the asset’s value decreases)
12. Owner’s Capital Introduced
Transaction: The owner introduces ₹50,000 in cash into the business as capital.
- Entry:
- Debit: Cash Account ₹50,000 (because cash is received)
- Credit: Capital Account ₹50,000 (because owner’s equity increases)
13. Drawing by Owner
Transaction: Owner withdrew ₹3,000 for personal use.
- Entry:
- Debit: Drawings Account ₹3,000 (because owner is taking money out, which decreases equity)
- Credit: Cash Account ₹3,000 (because cash is withdrawn)
14. Cash Deposit in Bank
Transaction: Deposited ₹8,000 into the bank.
- Entry:
- Debit: Bank Account ₹8,000 (because the bank balance increases)
- Credit: Cash Account ₹8,000 (because cash is decreased)
15. Salary Payment
Transaction: Paid ₹12,000 as salary to employees.
- Entry:
- Debit: Salary Expense Account ₹12,000 (because salary is an expense)
- Credit: Cash Account ₹12,000 (because cash is paid)
16. Rent Payment
Transaction: Paid ₹10,000 as rent.
- Entry:
- Debit: Rent Expense Account ₹10,000 (because rent is an expense)
- Credit: Cash/Bank Account ₹10,000 (because cash is paid
17. Utility Bill Payment (Electricity, Water, etc.)
Transaction: Paid ₹3,000 for the electricity bill.
- Entry:
- Debit: Utility Expense Account ₹3,000 (because utility is an expense)
- Credit: Cash/Bank Account ₹3,000 (because cash is paid)
18. Insurance Payment
Transaction: Paid ₹8,000 for an insurance premium.
- Entry:
- Debit: Insurance Expense Account ₹8,000 (because insurance is an expense)
- Credit: Cash/Bank Account ₹8,000 (because cash is paid)
19. Advertising Expense
Transaction: Paid ₹12,000 for advertising.
- Entry:
- Debit: Advertising Expense Account ₹12,000 (because advertising is an expense)
- Credit: Cash/Bank Account ₹12,000 (because cash is paid)
20. Interest on Loan Payment
Transaction: Paid ₹1,500 as interest on a loan.
- Entry:
- Debit: Interest Expense Account ₹1,500 (because interest is an expense)
- Credit: Cash/Bank Account ₹1,500 (because cash is paid)
21. Professional Fees
Transaction: Paid ₹6,000 as professional fees for legal services.
- Entry:
- Debit: Professional Fees Expense Account ₹6,000 (because professional fees are an expense)
- Credit: Cash/Bank Account ₹6,000 (because cash is paid)
22. Bad Debts Expense
Transaction: Wrote off bad debts worth ₹4,000.
- Entry:
- Debit: Bad Debts Expense Account ₹4,000 (because bad debts are an expense)
- Credit: Accounts Receivable ₹4,000 (because the receivable is written off)
23. Repairs and Maintenance Expense
Transaction: Paid ₹2,500 for repairs and maintenance of office equipment.
- Entry:
- Debit: Repairs and Maintenance Expense Account ₹2,500 (because repairs are an expense)
- Credit: Cash/Bank Account ₹2,500 (because cash is paid)
24. Bank Loan Received
Transaction: Received ₹50,000 as a bank loan.
- Entry:
- Debit: Bank Account ₹50,000 (because cash is received in the bank)
- Credit: Bank Loan Account ₹50,000 (because liability is created)
25. Bank Loan Repayment
Transaction: Paid ₹10,000 as repayment of the bank loan.
- Entry:
- Debit: Bank Loan Account ₹10,000 (because the liability decreases)
- Credit: Bank Account ₹10,000 (because cash is paid from the bank)
Here are 100 basic to advanced accounting entries with examples. This will cover various types of transactions you might encounter in everyday business accounting.
Basic Entries (1-20)
- Cash Sales
- Transaction: Sold goods worth ₹10,000 in cash.
- Entry:
- Debit: Cash ₹10,000
- Credit: Sales ₹10,000
- Credit Sales
- Transaction: Sold goods worth ₹15,000 on credit.
- Entry:
- Debit: Accounts Receivable ₹15,000
- Credit: Sales ₹15,000
- Cash Purchases
- Transaction: Purchased goods worth ₹8,000 in cash.
- Entry:
- Debit: Purchases ₹8,000
- Credit: Cash ₹8,000
- Credit Purchases
- Transaction: Purchased goods worth ₹12,000 on credit.
- Entry:
- Debit: Purchases ₹12,000
- Credit: Accounts Payable ₹12,000
- Rent Payment
- Transaction: Paid ₹5,000 as rent.
- Entry:
- Debit: Rent Expense ₹5,000
- Credit: Cash ₹5,000
- Salary Payment
- Transaction: Paid ₹20,000 as salary.
- Entry:
- Debit: Salary Expense ₹20,000
- Credit: Cash ₹20,000
- Cash Deposit
- Transaction: Deposited ₹30,000 in the bank.
- Entry:
- Debit: Bank ₹30,000
- Credit: Cash ₹30,000
- Cash Withdrawal
- Transaction: Withdrew ₹10,000 from the bank for business use.
- Entry:
- Debit: Cash ₹10,000
- Credit: Bank ₹10,000
- Owner’s Capital Contribution
- Transaction: Owner contributes ₹50,000 in capital.
- Entry:
- Debit: Bank ₹50,000
- Credit: Capital ₹50,000
- Owner’s Capital Withdrawal
- Transaction: Owner withdrew ₹15,000.
- Entry:
- Debit: Drawings ₹15,000
- Credit: Cash ₹15,000
- Interest Income
- Transaction: Received ₹2,000 as interest income.
- Entry:
- Debit: Bank ₹2,000
- Credit: Interest Income ₹2,000
- Interest Expense
- Transaction: Paid ₹1,000 as interest.
- Entry:
- Debit: Interest Expense ₹1,000
- Credit: Bank ₹1,000
- Utility Payment
- Transaction: Paid ₹3,500 for utilities.
- Entry:
- Debit: Utility Expense ₹3,500
- Credit: Cash ₹3,500
- Office Supplies
- Transaction: Purchased office supplies worth ₹4,000.
- Entry:
- Debit: Office Supplies ₹4,000
- Credit: Cash ₹4,000
- Insurance Payment
- Transaction: Paid ₹8,000 for insurance.
- Entry:
- Debit: Insurance Expense ₹8,000
- Credit: Cash ₹8,000
- Purchase Return
- Transaction: Returned goods worth ₹2,000.
- Entry:
- Debit: Accounts Payable ₹2,000
- Credit: Purchase Returns ₹2,000
- Sales Return
- Transaction: A customer returned goods worth ₹1,500.
- Entry:
- Debit: Sales Returns ₹1,500
- Credit: Accounts Receivable ₹1,500
- Prepaid Expenses
- Transaction: Paid ₹5,000 in advance for a service.
- Entry:
- Debit: Prepaid Expenses ₹5,000
- Credit: Cash ₹5,000
- Depreciation
- Transaction: Depreciation for the month is ₹3,000.
- Entry:
- Debit: Depreciation Expense ₹3,000
- Credit: Accumulated Depreciation ₹3,000
- Wages Payable
- Transaction: Wages of ₹7,000 are due.
- Entry:
- Debit: Wages Expense ₹7,000
- Credit: Wages Payable ₹7,000
Intermediate Entries (21-40)
- Goods Sold on Credit
- Transaction: Sold goods worth ₹18,000 on credit.
- Entry:
- Debit: Accounts Receivable ₹18,000
- Credit: Sales ₹18,000
- Sales Tax Payable
- Transaction: Sales tax of ₹1,800 is payable.
- Entry:
- Debit: Accounts Receivable ₹1,800
- Credit: Sales Tax Payable ₹1,800
- Tax Payment
- Transaction: Paid ₹6,000 in taxes.
- Entry:
- Debit: Tax Expense ₹6,000
- Credit: Cash ₹6,000
- Bank Loan Received
- Transaction: Received a bank loan of ₹50,000.
- Entry:
- Debit: Bank ₹50,000
- Credit: Bank Loan ₹50,000
- Bank Loan Repayment
- Transaction: Repaid ₹10,000 of the loan.
- Entry:
- Debit: Bank Loan ₹10,000
- Credit: Bank ₹10,000
- Dividends Declared
- Transaction: Declared ₹8,000 in dividends.
- Entry:
- Debit: Retained Earnings ₹8,000
- Credit: Dividends Payable ₹8,000
- Dividends Paid
- Transaction: Paid ₹8,000 in dividends.
- Entry:
- Debit: Dividends Payable ₹8,000
- Credit: Bank ₹8,000
- Capital Raised by Issuing Shares
- Transaction: Raised ₹20,000 by issuing shares.
- Entry:
- Debit: Bank ₹20,000
- Credit: Share Capital ₹20,000
- Loan Interest Payment
- Transaction: Paid ₹2,000 interest on the loan.
- Entry:
- Debit: Interest Expense ₹2,000
- Credit: Bank ₹2,000
- Accrued Salaries
- Transaction: Accrued salaries of ₹5,000.
- Entry:
- Debit: Salary Expense ₹5,000
- Credit: Accrued Salaries ₹5,000
- Bad Debts Written Off
- Transaction: Written off ₹3,000 as bad debts.
- Entry:
- Debit: Bad Debts Expense ₹3,000
- Credit: Accounts Receivable ₹3,000
- Stock Adjustment
- Transaction: Adjusted inventory value by ₹2,500.
- Entry:
- Debit: Inventory ₹2,500
- Credit: Stock Adjustment ₹2,500
- Inventory Purchase
- Transaction: Purchased inventory worth ₹15,000.
- Entry:
- Debit: Inventory ₹15,000
- Credit: Accounts Payable ₹15,000
- Inventory Sale
- Transaction: Sold inventory worth ₹10,000.
- Entry:
- Debit: Accounts Receivable ₹10,000
- Credit: Revenue from Sale of Goods ₹10,000
- Income from Investment
- Transaction: Earned ₹4,000 income from investment.
- Entry:
- Debit: Bank ₹4,000
- Credit: Investment Income ₹4,000
- Fixed Asset Purchase
- Transaction: Purchased machinery worth ₹30,000.
- Entry:
- Debit: Machinery ₹30,000
- Credit: Bank ₹30,000
- Fixed Asset Sale
- Transaction: Sold machinery worth ₹20,000.
- Entry:
- Debit: Bank ₹20,000
- Credit: Machinery ₹20,000
- Amortization of Intangible Assets
- Transaction: Amortized ₹2,000 on patents.
- Entry:
- Debit: Amortization Expense ₹2,000
- Credit: Accumulated Amortization ₹2,000
- Accrued Interest
- Transaction: Accrued ₹500 interest on loan.
- Entry:
- Debit: Interest Expense ₹500
- Credit: Interest Payable ₹500
- Tax Refund
- Transaction: Received ₹3,000 tax refund.
- Entry:
- Debit: Bank ₹3,000
- Credit: Tax Receivable ₹3,000
Advanced Entries (41-60)
- Capital Expenditure
- Transaction: Spent ₹25,000 on renovating office space.
- Entry:
- Debit: Renovation Expense ₹25,000
- Credit: Bank ₹25,000
- Share Issue Expenses
- Transaction: Spent ₹2,000 on issuing shares.
- Entry:
- Debit: Share Issue Expense ₹2,000
- Credit: Bank ₹2,000
- Discount Received
- Transaction: Received ₹1,000 discount on purchases.
- Entry:
- Debit: Accounts Payable ₹1,000
- Credit: Discount Received ₹1,000
- Discount Allowed
- Transaction: Allowed ₹500 discount on a sale.
- Entry:
- Debit: Discount Allowed ₹500
- Credit: Accounts Receivable ₹500
- Bonus Paid
- Transaction: Paid ₹10,000 as bonus to employees.
- Entry:
- Debit: Bonus Expense ₹10,000
- Credit: Bank ₹10,000
- Contingent Liability
- Transaction: Recognized contingent liability of ₹5,000.
- Entry:
- Debit: Contingent Liability Expense ₹5,000
- Credit: Contingent Liability ₹5,000
- Provision for Doubtful Debts
- Transaction: Created provision for doubtful debts of ₹2,000.
- Entry:
- Debit: Provision for Doubtful Debts ₹2,000
- Credit: Allowance for Doubtful Debts ₹2,000
- Payment of Long-Term Debt
- Transaction: Paid ₹20,000 on long-term debt.
- Entry:
- Debit: Long-Term Debt ₹20,000
- Credit: Bank ₹20,000
- Purchase of Bonds
- Transaction: Purchased bonds worth ₹10,000.
- Entry:
- Debit: Investment in Bonds ₹10,000
- Credit: Bank ₹10,000
- Revenue from Sale of Fixed Asset
- Transaction: Sold fixed asset worth ₹15,000.
- Entry:
- Debit: Bank ₹15,000
- Credit: Gain on Sale of Asset ₹15,000
- Refund from Supplier
- Transaction: Received ₹1,500 refund from supplier.
- Entry:
- Debit: Cash ₹1,500
- Credit: Purchase Returns ₹1,500
- Refund to Customer
- Transaction: Issued ₹2,000 refund to customer.
- Entry:
- Debit: Sales Returns ₹2,000
- Credit: Cash ₹2,000
- Prepaid Rent
- Transaction: Paid ₹12,000 for 12 months rent in advance.
- Entry:
- Debit: Prepaid Rent ₹12,000
- Credit: Bank ₹12,000
- Unearned Revenue
- Transaction: Received ₹3,000 for services to be performed in the future.
- Entry:
- Debit: Bank ₹3,000
- Credit: Unearned Revenue ₹3,000
- Sales of Intangible Assets
- Transaction: Sold a patent for ₹5,000.
- Entry:
- Debit: Bank ₹5,000
- Credit: Patent ₹5,000
- Loan from Shareholder
- Transaction: Received ₹10,000 loan from shareholder.
- Entry:
- Debit: Bank ₹10,000
- Credit: Loan Payable ₹10,000
- Goods Sent on Consignment
- Transaction: Sent goods worth ₹8,000 on consignment.
- Entry:
- Debit: Consignment Account ₹8,000
- Credit: Inventory ₹8,000
- Bank Charges
- Transaction: Bank charged ₹500 service fees.
- Entry:
- Debit: Bank Charges ₹500
- Credit: Bank ₹500
- Loss on Sale of Asset
- Transaction: Sold equipment at a loss of ₹2,000.
- Entry:
- Debit: Loss on Sale of Asset ₹2,000
- Credit: Equipment ₹2,000
- Purchase of Inventory on Credit
- Transaction: Purchased inventory worth ₹5,000 on credit.
- Entry:
- Debit: Inventory ₹5,000
- Credit: Accounts Payable ₹5,000
वाउचर क्या है और लेखांकन & Tally में इसका उपयोग कैसे किया जाता है
